What Are Synthetic Phonics And Why You Should Use It In Your Classroom

What Is Synthetic Phonics
So exactly what are synthetic phonics, you might be wondering? This buzzword has been popping up more and more. Keep reading to find out exactly what Synthetic Phonics are and how you can use it in your class.
Synthetic Phonics is a fancy name for the explicit direct instruction used to teach – you guessed it … Phonics.
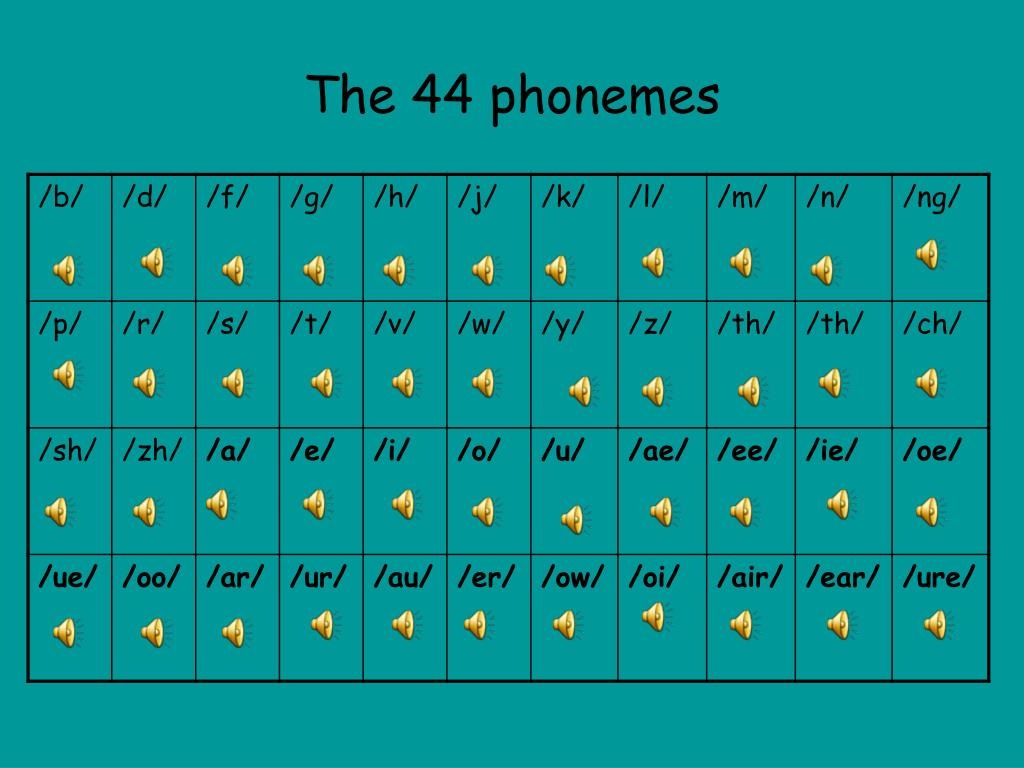
Instead of using all those “spelling rules” that have just as many exceptions as they do words that follow them. All 44 sounds in the English language are taught sequentially, building from simple sounds and easy to decode sounds to the more complex ones.

I have been teaching systematic synthetic phonics for the last 6 or so years of teaching and it really works! It is amazing to see the progress that young learners make when I really explain to them all the different ways the 44 sounds can be represented. The best thing about synthetic phonics is it caters to all students in my classroom. Every class I have ever taught has had a massive variety of academic abilities and a number of students with diagnosed and undiagnosed learning difficulties. Teaching phonics using the synthetic phonics approach means that I am supporting all their needs and it’s quite easy to do once you know how!
If you want some great phonics resources to help you teach synthetic phonics I have so many products in my shop for you to use. You can even download a freebie to see if you like it!
What Does Synthetic Phonics Instruction Involve?
Synthetic phonics is a way of teaching spelling where words are broken down to the smallest units of sound called phonemes. Students learn to represent the sounds in language using the letters also called graphemes. Synthetic phonics involves students learning to identify all of the small sounds in a word and match them to a letter. This breaking down of the words is called decoding.
Synthetic Phonics instruction involves a few key elements;
- Students are taught all 44 phonemes in the English language.
- It is explicitly taught.
- Systematic teaching of the 44 phonemes becomes more complex as students move through the grade levels.
- Synthetic phonics provides a consistent approach to teaching phonics so the message about how to read and spell is consistent across the grade levels.
- It is quick and efficient, students are not taught a sound a week, they learn a group of phonemes so they can begin learning spelling and reading straight away.
- Students are taught to blend sounds in a word to read and to listen for the sounds in a word to spell.
- All the different ways a sound can be represented are taught. For example the sound /a/ can be spelled a, ay, ai, eigh and so on.
- Words that are not decodable, but are high frequency words are taught explicitly.
- Students are taught the sounds first and then the letter names
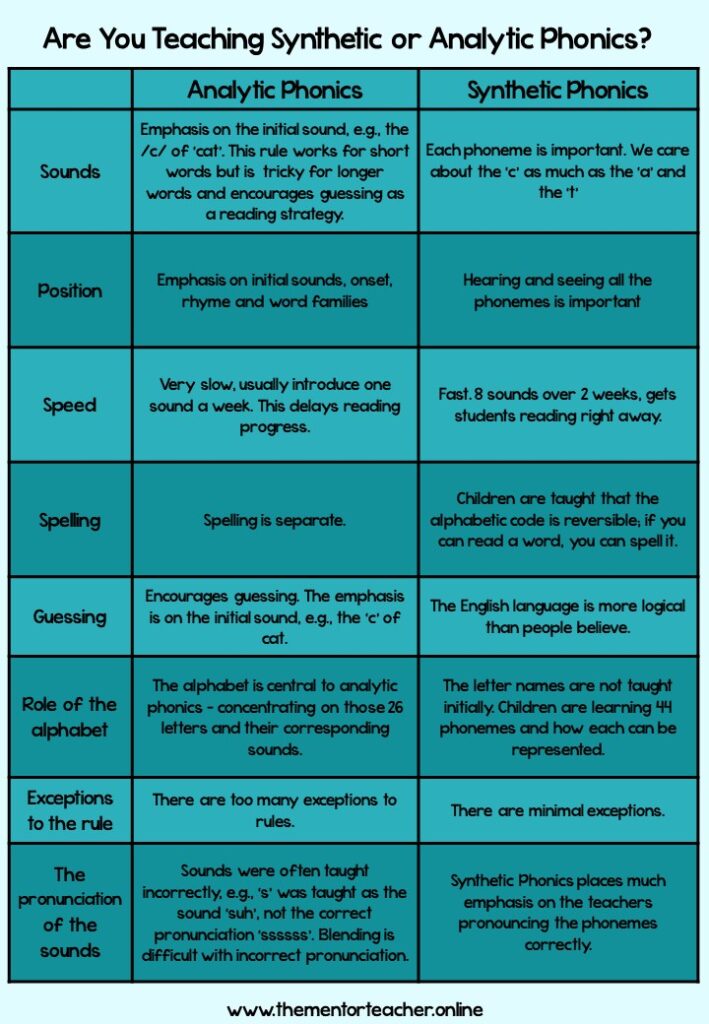
Synthetic Phonics vs Analytic Phonics
There are two different ways of teaching phonics and they are synthetic phonics and analytic phonics. They differ in many ways and the difference can affect how quickly students learn to read and spell.
In the past students were taught to read and spell using ‘analytic phonics’. This method has children ‘analysing a word’, taking clues from recognition of the whole word, the initial sound, and the context. This is a hit-and-miss approach that encourages guessing as a reading strategy! Students were being taught Analytic Phonics in the USA, Australia, and the UK and there are significant numbers of children failing to learn to read as well as they should; 38%, 20%, and 20% respectively! Synthetic Phonics involves no guessing. It is the synthesising, or blending of phonemes (sounds) to make a word, enabling children to read. Synthetic phonics is quick and efficient. Students are taught the letter sounds as soon as they start school before they can learn to read. Using an analytic phonics approach students are taught to recognise whole words by sight and then break down the word into units of sounds. Letter sounds are not taught until after students begin to learn to read. Students can find it more difficult to identify the sounds when being taught using an analytic phonics approach because it is not explicit.
Synthetic Phonics Programs
There are many different Synthetic Phonics programmes and they all teach the same set of sounds. Like all teaching programmes each has a few differences. For example, all have their own order of introducing the sounds. Studies show that the order doesn’t matter too much. They generally introduce consonants and short vowel sounds first. Then long vowels, digraphs, adjacent consonants, and r-controlled vowel sounds (such as /er/ and /or/). Students learn one way of representing each of the sounds and then are slowly shown the spelling alternatives for each. For example, students learn that the /s/ sound is written down using the letter ‘s’ (as in sat). Later on, students learn that we can write the /s/ sound using the letter ‘c’ (as in city) or ‘sc’ (as in science), and the /s/ sound using the letters ‘ps’ (as in psychic) or ‘st’ (as in listen).
Some synthetic phonics programmes you might like to check out are;
Synthetic Phonics and Learning Difficulties
Students can find it difficult to learn to read and spell for so many reasons. While language is a built-in skill that all humans possess, reading, writing, and spelling is not an innate ability. It is something that people have developed and learned over many hundreds of years. For most students, a structured programme that includes systematic synthetic phonics and explicit teaching will be successful. Some students do have learning difficulties that mean learning to read and spell extremely difficult. Students who have poor memory skills, find it is difficult for them to remember what they have been taught. These students can have great difficulty segmenting words into individual speech sounds, making it difficult to link phonemes (speech sounds) to graphemes (letters). These children will find learning to read and spell difficult whatever method is used.

When Synthetic Phonics is taught in a systematic and explicit way, is the approach most likely to result in successful outcomes. Children with a specific learning disorder in reading stand out as their reading ability does not match their expected abilities. Read more about Dyslexia here. Learning to read and spell can be a frustrating journey. Students are usually successful using a Synthetic Phonics approach.
Teaching Using The Synthetic Phonics Approach
Learning to read, write and spell is not an innate human ability, it takes time for students to master these skills. It is so important that children are ready to begin learning before we start teaching phonics. Students are ready when they can;
- Listen carefully to the sounds in our speech.
- Be able to make the sounds they hear.
- Children can sequence the sounds they hear in a word.
When students are ready, start with letter and sound correspondence. It is important to remember the following
- Letter names vs Letter Sounds. When using a Synthetic phonics approach teach the letter sounds not names, as it is confusing.
- Letters don’t make the sounds. There are 44 sounds in the English language and only 26 letters.I t is important that students understand that the letters don’t make the sounds, they simply represent them.
- Pronunciation. It is important to avoid mispronouncing the sounds, or making the lazy vowel or schwa sound at the end of a sound. For example, when pronouncing the /k/ sound, make it crisp and short, rather than adding in an extra -uh sound at the end.
Below are some general teaching points to make sure your phonics lessons are a hit with your students.
- Keep phonics lessons short – 15 to 20 minutes is perfect.
- Take a consistent approach – make sure you are systematically teaching phonics.
- Move through the sounds quickly – Moving quickly through your phonics programme will produce the best results. Don’t worry you can come back and revise anything students are struggling with.
- Make it fun – Use lots of fun and engaging activities so students love learning to read and spell.
If you want some great phonics resources, I have so many products in my shop for you to use. You can even download a freebie to see if you like it!
Want to know more about teaching using Synthetic Phonics? This is how I use the Letters and Sounds Phonics Programme in my classroom – read my blog post here.